Have you ever imagined losing access to all your digital files in an instant? Unfortunately, this nightmare scenario has become a reality for many due to ransomware attacks. But with the right knowledge and precautions, you can significantly reduce your risk.
Let's dive into the world of ransomware prevention.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts your files, holding them hostage until you pay a ransom. It's like a digital locksmith gone rogue, changing all your locks and demanding payment for the keys. But unlike a physical locksmith, these cyber criminals often fail to deliver even after payment.
The Threat Landscape
Ransomware attacks have surged in recent years, painting a grim picture of our digital vulnerability. In 2021 alone, global ransomware damage costs were estimated to exceed £15,7 billion. Even more alarming, experts project this figure to skyrocket to a staggering £208.7 billion by 2031. This isn't just a problem for large corporations - it's a threat that touches businesses of all sizes.
Consider this: in 2021, 37% of all businesses and organizations fell victim to ransomware attacks. That's more than one in three companies facing this digital threat. The financial toll? Recovering from a ransomware attack cost businesses an average of £1.45 million in 2021.
But here's the kicker - paying the ransom doesn't guarantee a happy ending. Of all ransomware victims, 32% cave to the demands and pay up. Yet, on average, they only recover 65% of their data. It's a digital gamble with unfavorable odds.
The Importance of Preparation
Given these sobering statistics, you might think that having a solid backup strategy would be a universal practice. Surprisingly, only 57% of businesses successfully recover their data using backups. This underscores a critical point: it's not enough to have backups; they must be secure, up-to-date, and regularly tested.
The ransomware threat continues to evolve and intensify. In 2023, there was a 27% increase in companies falling victim to ransomware attacks compared to the previous year. Despite the risks, only 8% of companies paid the ransom when attacked - a sign that more organizations are heeding warnings about the perils of paying criminals.
Beyond Ransomware: A Broader Cybersecurity Challenge
While ransomware grabs headlines, it's part of a larger cybersecurity landscape that's growing increasingly treacherous. Consider these eye-opening facts:
- 43% of enterprises failed a compliance audit in 2023, with those companies 10 times more likely to suffer a data breach.
- Human error was identified as the top cause of data breaches for the second year in a row.
- A staggering 93% of IT professionals believe security threats are increasing in volume or severity, a significant rise from 47% the previous year.
- Malware was the fastest-growing threat in 2023, with 41% of enterprises witnessing a malware attack.
Perhaps most concerning is this: only 33% of organizations are able to fully classify all of their data, with 16% stating that they classify very little or none of their data. How can we protect what we don't even know we have?
The Path Forward
These statistics paint a challenging picture, but they also illuminate the path forward. Robust cybersecurity practices, regular training to mitigate human error, and comprehensive data classification and protection strategies are no longer optional - they're essential for survival in our digital age.
In the following sections, we'll explore practical steps you can take to fortify your defences against ransomware and other cyber threats. Remember, when it comes to cybersecurity, prevention is better than cure - or in this case, better than millions of pounds in potential damages.
Stay tuned as we delve deeper into effective ransomware prevention strategies, backup best practices, and how to create a culture of cybersecurity awareness in your organisation. Your digital future may depend on it.
Prevention Strategies
1. Keep Your Systems Updated
Just as you wouldn't leave your front door unlocked, don't leave your software vulnerable. Regular updates patch security holes that ransomware could exploit.
Key Actions:
- Enable automatic updates for your operating system
- Keep all software, especially security software, up-to-date
- Replace outdated systems that no longer receive security updates
Example Update Schedule:
| Software Type | Update Frequency |
|---|---|
| Operating System | As soon as available (enable auto-updates) |
| Antivirus/Security Software | Daily |
| Web Browsers | Weekly |
| Other Applications | Monthly or as updates become available |
💡 Pro Tip: Set aside a specific time each week to check for and install updates across all your devices.
2. Backup Your Data
Imagine having a spare key hidden away when a locksmith tries to extort you. That's what a good backup strategy does for your data.
The 3-2-1 Backup Rule:
- Keep at least 3 copies of your data
- Store 2 backup copies on different storage media
- Keep 1 backup copy offsite
Backup Methods:
- Cloud Storage: Services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or iCloud
- External Hard Drives: Physical devices you can disconnect from your network
- Network Attached Storage (NAS): A dedicated file storage system connected to your network
💡 Pro Tip: Regularly test your backups by attempting to restore files. A backup is only as good as its ability to be restored!
3. Be Wary of Phishing Attempts
Phishing emails are like wolves in sheep's clothing, often the initial vector for ransomware attacks.
Red Flags in Emails:
- Urgent or threatening language
- Requests for sensitive information
- Unexpected attachments
- Links to unfamiliar websites
- Poor grammar or spelling
Example: Spotting a Phishing Email
From: amazonsecurity@am4zon.comSubject: URGENT: Your account has been locked!Dear Valued Customer, Your Amazon account has been locked due to suspicious activity. Click the link below to verify your identity and unlock your account immediately:
[Suspicious Link]
Failure to do so within 24 hours will result in permanent account closure.
Best regards, Amazon Security Team
Can you spot the red flags? (Hint: Check the sender's email, the urgent tone, and the suspicious link)
💡 Pro Tip: When in doubt, go directly to the company's website by typing the URL in your browser, rather than clicking any links in the email.
4. Implement Strong Access Controls
Think of access controls as the bouncers of your digital nightclub. They decide who gets in and what they can do.
Password Best Practices
- Use long, complex passwords (at least 12 characters)
- Avoid common words or phrases
- Use a unique password for each account
- Consider using a password manager
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Methods
- Something you know (password)
- Something you have (phone or security key)
- Something you are (fingerprint or face recognition)
💡 Pro Tip: Use app-based authenticators (like Google Authenticator or Authy) instead of SMS for stronger security.
5. Employee Education
Your team can be your strongest defense or your weakest link. Regular training turns them into cyber-sentinels.
Key Training Topics
- Identifying phishing attempts
- Safe browsing habits
- Proper handling of sensitive data
- Incident reporting procedures
Engagement Ideas
- Gamify cybersecurity training with quizzes and rewards
- Share real-world examples and case studies
- Conduct regular simulated phishing tests
💡 Pro Tip: Create a cybersecurity newsletter to keep employees informed about the latest threats and best practices.
6. Network Segmentation
Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Network segmentation limits the spread of an attack if one occurs.
Segmentation Strategies:
- Physical Segmentation: Separate hardware for different network segments
- Logical Segmentation: Using VLANs to create virtual network segments
- Functional Segmentation: Grouping similar assets or functions together
Example Segmentation Plan:
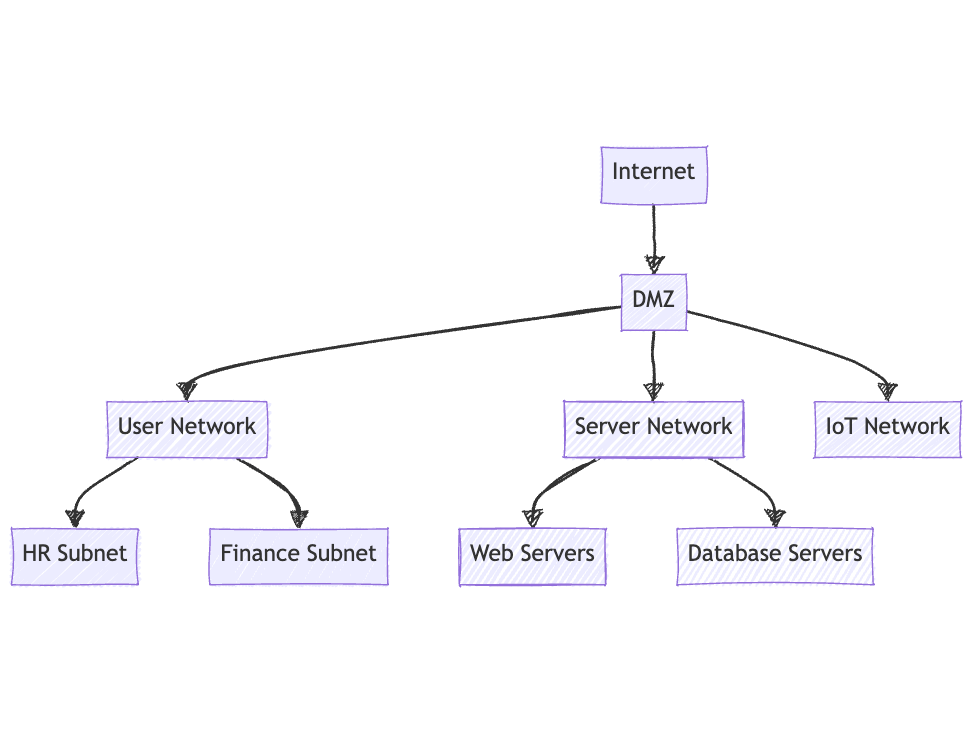
Let's break down this network segmentation plan:
Internet: The entry point for all external traffic.
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone):
- Acts as a buffer between the public internet and internal networks.
- Hosts public-facing services like web servers and email gateways.
- Provides an additional layer of security for internal networks.
User Network:
- Contains employee workstations and devices.
- Subdivided into department-specific subnets for granular access control:
- HR Subnet: Restricted access to sensitive employee data.
- Finance Subnet: Isolated to protect financial information and systems.
Server Network:
- Houses internal servers and critical infrastructure.
- Separated from user networks to limit potential attack vectors.
- Further segmented into:
- Web Servers: For internal web applications.
- Database Servers: Isolated to protect sensitive data.
IoT Network:
- Dedicated network for Internet of Things devices.
- Separated due to potentially lower security standards of IoT devices.
Benefits of this segmentation:
- Limits the spread of malware or ransomware if one segment is compromised.
- Allows for tailored security policies for each network segment.
- Simplifies compliance by isolating regulated data (e.g., in HR and Finance subnets).
- Improves overall network performance by managing traffic flow between segments.
💡 Pro Tip: Regularly review and update your network segmentation plan to ensure it aligns with your current business needs and security requirements. Consider using Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW) to manage traffic between segments and implement advanced threat protection.
7. Incident Response Plan
Hope for the best, but prepare for the worst. An incident response plan is your battle strategy against ransomware.
Key Components of an Incident Response Plan:
- Preparation: Develop policies, response procedures, and communication strategies
- Identification: Detect and analyze potential incidents
- Containment: Isolate affected systems to prevent further damage
- Eradication: Remove the threat and its artifacts
- Recovery: Restore systems and data from clean backups
- Lessons Learned: Review the incident and improve your defenses
Example Incident Response Flowchart:
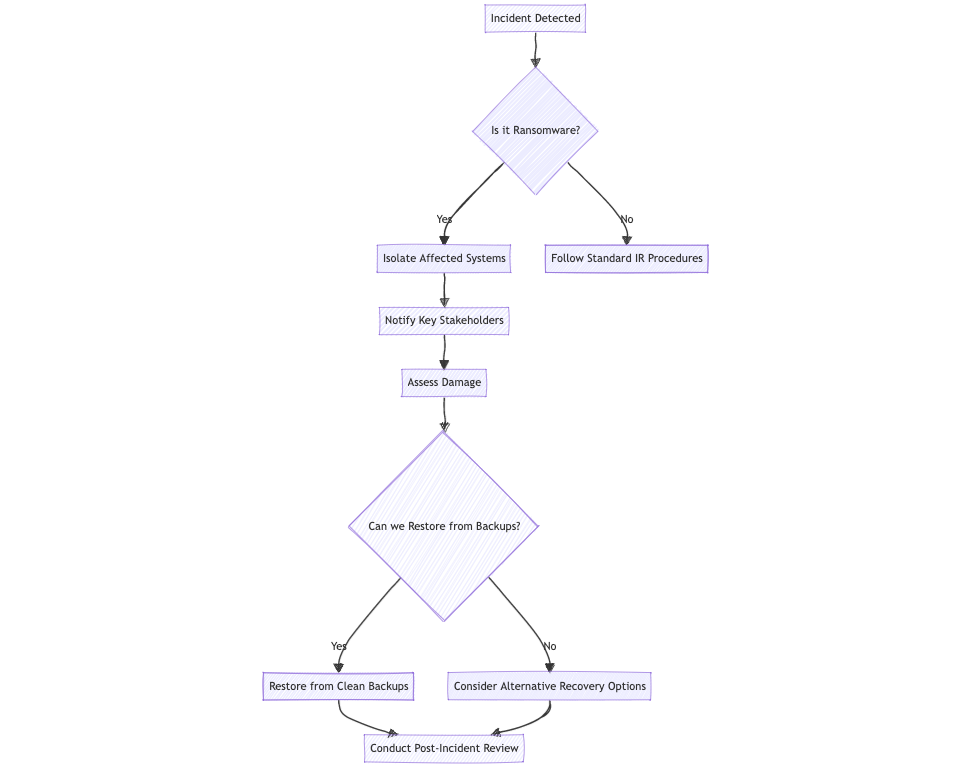
Let's break down this incident response flowchart:
💡 Pro Tip: Conduct regular tabletop exercises to test your incident response plan and ensure all team members understand their roles.
What If You're Attacked?
If you find yourself facing a ransomware attack, don't panic. Here's what to do:
- Isolate the infected systems
- Report the incident to law enforcement
- Restore from clean backups if available
- Seek professional help if needed
Remember, paying the ransom doesn't guarantee you'll get your data back and may encourage further attacks.
Conclusion
In the digital age, ransomware is a serious threat, but it's not invincible. By implementing these strategies and staying vigilant, you can significantly reduce your risk. Like a well-trained martial artist, you'll be prepared to defend against cyber threats.
Stay safe, stay informed, and remember: when it comes to ransomware, prevention is always better than cure.
